Meltblown fabric is a type of non-woven fabric that is made by melting thermoplastic materials and then using high-speed air flow to stretch and draw the fibers into a fine web. This process creates a fabric with unique properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
The primary use of meltblown fabric is in filtration. The fine fibers in the fabric create a dense network that traps particles and contaminants from air or liquid flows. Meltblown fabric is commonly used in air and liquid filtration systems, including air conditioning filters, surgical masks, and personal protective equipment like N95 respirators.
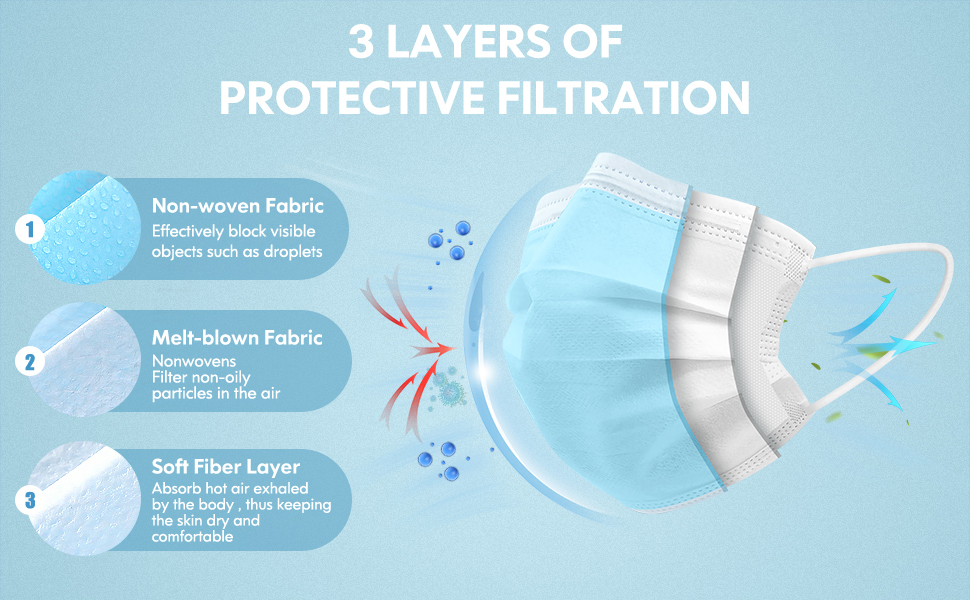
Meltblown fabric is also used in a variety of other applications. It is commonly used in the production of absorbent materials like diapers, sanitary napkins, and wet wipes. The fine fibers in the fabric are able to absorb large amounts of liquid, making it an ideal material for these products.
Additionally, meltblown fabric is used in the production of industrial textiles. The fabric is resistant to chemicals and provides excellent barrier properties, making it ideal for use in protective clothing, industrial filters, and other applications where resistance to chemicals, heat, or other environmental factors is important.
One of the unique properties of meltblown fabric is its ability to be molded into different shapes and textures. The fabric can be embossed or textured to create surfaces with different levels of slip resistance or to provide bulk for cushioning or padding. This makes it an ideal material for use in automotive interiors, furniture padding, and other applications where comfort or slip resistance is important.
The production of meltblown fabric is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and expertise. The process begins with the selection of the appropriate thermoplastic materials. The materials are then melted and extruded through a spinneret, which is a specialized nozzle that creates a fine stream of molten material.

The stream of molten material is blown by high-speed air flow, which stretches and draws the fibers into a fine web. The web is then subjected to various treatments to improve its properties. For example, the web may be subjected to electrostatic charging to increase its ability to trap particles and contaminants.
One of the challenges of producing meltblown fabric is maintaining consistent properties across the fabric. The properties of the fabric, such as its pore size, density, and particle capture efficiency, are critical to its performance in filtration applications. To achieve consistent properties, the process must be carefully controlled and monitored.
Despite the challenges, meltblown fabric is an important material in many industries. Its ability to filter particles and contaminants makes it an essential component of air and liquid filtration systems. Its absorbent properties make it an ideal material for use in personal care and hygiene products. And its resistance to chemicals and other environmental factors make it an ideal material for use in industrial textiles.
Meltblown fabric is a unique material that is used in a wide range of applications. Its ability to filter particles and contaminants, absorb large amounts of liquid, and resist chemicals and other environmental factors make it an essential component in many industries. The complex process of producing meltblown fabric requires expertise and specialized equipment, but the resulting material is critical to the performance of many products and systems.


