Over time, protective suits have become advanced in terms of material composition and protection performance. There are different types of protective suits, each designed to cater to different hazards and situations. One thing you may have noticed is that some protective suits have the letter “B” added next to their name, such as “4B” or “3B”. But what exactly does the B means to protective suit types?
To understand what the “B” denotes, it’s essential to first understand the European clothing protection levels, which are based on various factors such as barrier and degradation resistance, liquid, particle, and gaseous protection, and durability.
According to the European Norm 14605: 2005, there are six types of protective clothing levels, namely Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4, Type 5 and Type 6. Additionally, there are ensembles that combine elements of two or more of these types to offer more comprehensive protection. These ensembles are Types 3-B, 4-B, 5-B, and 6-B.
Type 1 protective clothing provides protection against chemical and biological hazards, with a full-body, air-tight design that provides the highest level of protection for workers. Type 2 protective clothing provides chemical and biological protection to the wearer but is open at the back to allow for better air circulation. Type 3 protective clothing has a design that protects the wearer from sprays of liquids and particles, with an air-tight coverall that has an attached hood, gloves, and boots.
Type 4 protective clothing provides protection against sprays of particulate matter and low-pressure liquid. It does not provide protection against chemicals or biological hazards but offers limited breathability and liquid resistance. Type 5 protective clothing protects the wearer against harmful dust particles and light liquid sprays with a low concentration of chemicals. Lastly, Type 6 protective clothing provides protection against minor splashes and sprays of chemicals, making it suitable for low-risk environments.
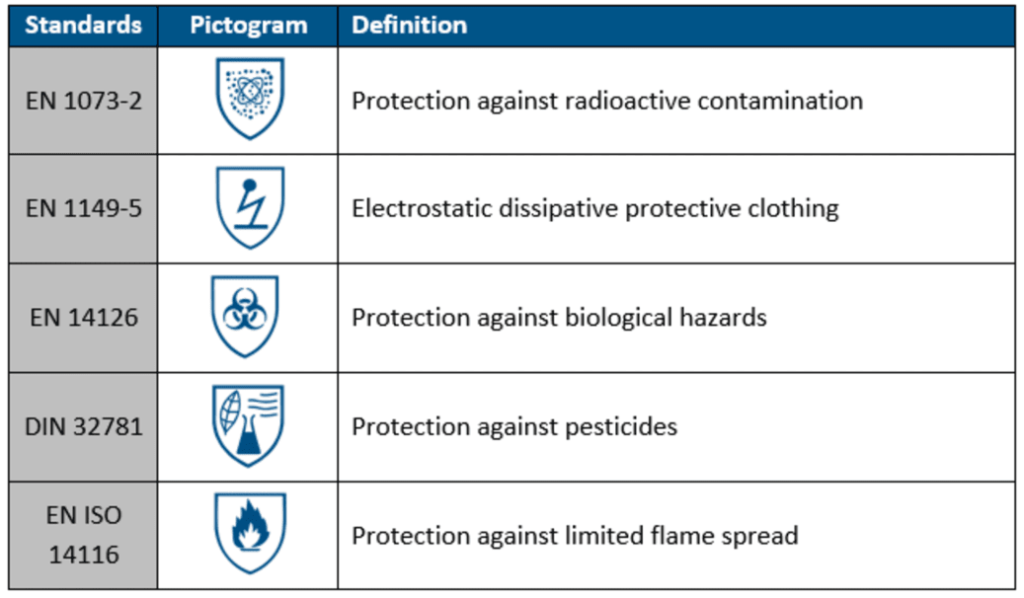
Now let’s discuss the “B” suffix. When added to the aforementioned types, the “B” stands for a higher level of protection concerning liquids. A “B” appended to the type number means that the suit offers limited protection against hazardous chemicals and gaseous agents. If overalls are certified in accordance with EN 14126, they meet the performance requirements against infectious agents and may be marked with the “B”. Here, it is important to note that the defined test procedures focus on the medium that contains the micro-organisms, such as fluids, aerosols or solid dust particles and not on specific viruses or bacteria. Overalls with taped seams provide a higher level of protection as the micro-organisms are small enough to penetrate through the tiny needle holes along the seam.
For example, a type 3B suit is similar to a Type 3 protective suit but with added protection against some chemicals and aerosols. This suit also provides limited breathability and is better suited to situations where there might be liquid hazards.
A 4B suit is similar to a Type 4 protective suit but can also provide limited protection against some gaseous agents and chemicals. This suit offers moderate breathability, and it is used in high-risk industrial settings where there might be chemical spills.
A type 5B suit is more breathable than a Type 5 protective suit and provides limited protection against some hazardous chemicals and gaseous agents. It replaces the traditional coveralls and is ideal for a range of activities that require protection against hazardous particulate matter.
Finally, a 6B suit provides low-level protection against some chemicals, aerosols, and particulate matter. It is mainly used in situations where there is a low risk of exposure to hazardous chemicals or bacterial or viral particles.

In conclusion, the “B” suffix added to types of protective suits denotes a higher level of liquid hazard protection. These suits are designed to protect workers from different types of liquid hazards and might offer limited protection against gaseous agents and chemicals.
When working in a hazardous environment, it’s essential always to wear the right protective clothing and equipment. Knowing the different types of protective clothing available and their level of protection can help you choose the suitable level of protection for the work environment you’re in. Additionally, employers must provide their employees with the appropriate protective clothing and equipment to ensure their safety while at work.


